GCP Products Overview
- Introduction
- Cloud Compute Engine
- gcloud
- GCP Storage Solutions
- IAM
- Cloud BigQuery
- Could Datalab
- Cloud Datastudio
- Cloud Pub/Sub
- Cloud Dataproc
- Cloud Dataflow
- Stackdriver
- Machine Learning/AI
Introduction
I have used Google Cloud Platform (GCP) quite a bit throughout my graduate research. GCP provides a wide range of online web services/products and I have used several of them. In this post, I’ll give an overview of most of the GCP products. Hopefully this post will help you (and me) understand the use cases of various products as well as the differences among similar products/names.
Cloud solutions allow businesses to shift their data and workload from on-premise IT servers onto off-premise servers that are usually stored in a Data Center.
Advantages of Cloud solutions include:
- No capital investment
- Immediate provisioning of required infrastructure
- No maintenance of the physical servers required
Cloud Compute Engine
Compute engine service is where we can create instances/compute nodes/virtual machines (VM) on GCP. This is one of the very few IaaS (infrastructure as a service) products that GCP offers. Most of the products on GCP are Paas (platform as a service) products.
A VM is like a computer having hard drive and memory however it does not have a graphical user interface like our computer screen. We can talk to it via the command line interface/shell etc.
Regions and Zones. Regions are locations around the world while Zones are locations inside the regions and represent physical data centers. Each zone is a single data center.
When we deploy VMs we deploy them in a region and a zone. Usually we deploy them to wherever is closet to our workload.
Memory and CPU options. Main categories are separated in: Micro, small, standard, highmem or high CPU.
Boot Disk Options. We can customize the disk capacity of the VM and choose the type, either a standard persistent disk or a Solid State Disk (SSD). Generally we will want to pick SSD as the cost is not that much different but performance with SSD is much better. Unless we want to store a lot of data on the VM but do not require fast input/output IO operations then think about using Standard disks.
Preemptible Instances. Preemptible instances are a pricing innovation for GCP Compute engine. A Preemptible VM is an instance that we can create and run at a much lower price than normal instances. However this comes with some setbacks.
Compute engine might terminate Preemptible instances at any time due to other people’s workload on GCP, it really depends on the usage at the time. Also, Preemptible instances always self terminate after they run for 24 hours.
Snapshots. Snapshots are used for backup operations or transfer of data. Snapshots are a copy of the disk in that moment of time when we take the Snapshot.
Whatever we have in the storage will be copied, so we can recover lost data if the primary disk fails or transfer contents to a new disk.
Images. When setting up a VM we must choose an Operating System image first. Popular images are Linux based such as Centos and Ubuntu. We can also save the VM disk as an image to be used later or create a new VM using a Snapshot that we have created.
Compute engine is useful if we just want to run an ad hoc function that is not incorporated into the other GCP PaaS products. For example if the app has a backend operation that requires extra work apart from the source code then using VMs on compute engine will be perfect.
gcloud
gcloud is a tool that provides the primary command-line interface to Google Cloud Platform. For example, to name a few, we can use gcloud to create and manage:
- Google Compute Engine virtual machine instances and other resources
- Google Cloud SQL instances
- Google Cloud Dataproc clusters and jobs
gcloud components
The gcloud components command group lets us control which tools are installed in the Cloud SDK. It can be used to install, update and remove components of the Cloud SDK, ensuring a clean, up-to-date installation. gcloud components regularly checks whether updates are available for the tools we already have installed, and gives us the opportunity to upgrade to the latest version.
gcloud components update- To update all components we have to their latest version.gcloud components list- To see all available components.gcloud components install <COMPONENT>- To install a component we don’t have.gcloud components remove <COMPONENT>- To remove a component we no longer need.
gcloud config
The gcloud config command group lets us set, view and unset properties used by Cloud SDK. A configuration is a set of properties that govern the behavior of gcloud and other Cloud SDK tools.
gcloud config GROUP | COMMAND [GCLOUD_WIDE_FLAG ...]
GROUPS
GROUPis one of the following:configurations- Manage the set of gcloud named configurations.
COMMANDS
COMMANDis one of the following:list- List Cloud SDK properties for the currently active configuration.set- Set a Cloud SDK property.unset- Unset a Cloud SDK property.get-value- Print the value of a Cloud SDK property.
AVAILABLE PROPERTIES
coreaccount- Account gcloud should use for authentication. Rungcloud auth listto see the currently available accounts.project- Project ID of the Cloud Platform project to operate on by default. This can be overridden by using the global--projectflag.disable_usage_reporting- If True, anonymous statistics on SDK usage will not be collected. This value is set by default based on your choices during installation, but can be changed at any time.
computeregion- Default region to use when working with regional Compute Engine resources.zone- Default zone to use when working with zonal Compute Engine resources.
dataprocregion- Cloud Dataproc region to use.
ml_enginelocal_python- Full path to the Python interpreter to use for Cloud ML Engine local predict/train jobs. If not specified, the default path is the one to the Python interpreter found on system PATH.
gcloud compute
The gcloud compute command group lets us create, configure and manipulate Google Compute Engine virtual machines.
COMMANDS
ssh <INSTANCE>- SSH into a virtual machine instance.
GCP Storage Solutions
GCP offers many PaaS Storage solutions for different types of data and access methods. The main products are as follows:
- Cloud Storage
- Cloud Datastore
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Spanner
- BigTable
- BigQuery
Cloud Storage
Cloud Storage is highly durable, stores data redundantly, highly available, infinite scalability and consistent. Mainly used for storing binary or object data such as images, audio, video and backups.
Cloud Storage offers different products for accessibility and archival. Different offerings are:
- Multi-Regional: Ideal for content that is required to be served across geographic regions.
- Regional: For use within a single region.
- Nearline: Used for data accessed less than once a month (Archival solution).
- Coldline: Used for data accessed less than once a year (Archival solution).
The pricing is most expensive for Multi-Regional to the cheapest for coldline as you would expect. One big difference in Google’s archival products such as nearline and coldline is that we can retrieve the stored data in less than a second while for Amazon’s Glacier (which is their archival solution) the retrieval time is (currently) a few hours.
Cloud Storage advantages:
- Large storage, potentially Petabytes of data.
- Can store images, audio, etc.
- Access like a file system.
- Can have various options to suit our needs.
Cloud Storage disadvantages:
- To access have to copy to local disk could affect performance.
- It stores files or blobs so cannot query by content.
Cloud Datastore
Cloud Datastore is a highly scalable and managed NoSQL database. Highly durable and available. Support ACID transactions (which is typical for most SQL data warehouse solutions), SQL-like queries.
Cloud datastore are mainly used for User profiles, such as social network profiles and game statuses.
Cloud Datastore advantages:
- Highly scalable, automatic sharding and replication (Highly available).
- Supports ACID transactions (consistent and durable).
- SQL like queries
- Can update attributes (or add attributes which are like columns and rows)
Cloud Datastore disadvantages:
- Not really any mentionable disadvantages just it is not suitable for some applications as there are better options.
Cloud SQL
Fully managed SQL database on GCP. Offers high performance, reliability, scalability, security etc. This is basically our standard SQL database but hosted on Google’s Platform which offers superior performance and reliability etc.
Cloud SQL advantages:
- SQL compatible
- Can update a field (so not only append)
Cloud SQL disadvantages:
- Small storage (only Gigabytes)
Cloud Spanner
Cloud Spanner is fully managed, scalable and highly available. Cloud Spanner is currently the only Cloud Storage solution that combines the benefits of a relational database with a non-relational database (NoSQL).
Traditionally, creating a database requires trade-offs. Relational databases are generally a more consistent way to store data and supports SQL transactions however the problem is with capacity.
The more data we store in a relational database the slower the database and typical SQL databases do not support big data. That’s the reason why we use NoSQL. NoSQL databases allow big data. However, it generally does not support SQL transactions and is non-relational, usually only key-value pairs.
This is why Cloud Spanner is considered magical, it allows traditional databases to scale combining the best of both worlds. Cloud Spanner can be used for many applications and industries. Basically anywhere a relational database is required but also needs to scale.
BigTable
BigTable is NoSQL, massively scalable (to the PetaBytes) Big Data database service. Same database that powers Google’s own services such as the Search engine and Google Maps.
BigTable is fully managed, highly durable and available, same as all other PaaS products. Mainly used to support high throughput and low latency workloads such as Internet of Things (IoT) and user analytics.
BigTable advantages:
- Huge Storage - Petabytes of data
- Autoscaling, Fully managed
- Low latency, high throughput
- Integrates easily with Big Data tools like Hadoop, Cloud Dataflow and Dataproc, HBase
BigTable disadvantages:
- Because of its low latency and high throughput it can potentially be much more costly
- Cannot modify data, put row only
- Does not support SQL Queries
BigQuery
This is Google’s Data-warehousing solution. It’s serverless/highly scalable and fully managed. Also it is low cost when storing. It is commonly used for Big Data analytics and forming data assets for dashboards.
BigQuery advantages:
- SQL compatible
- Cheap storage, costs come in form of query
- Scalable, fully managed, serverless
- Can update fields (not just append only like BigTable)
- Can support batched or streaming inserts. Streaming is more expensive of course.
BigQuery disadvantages:
- Can be very costly to operate if large amount of data is to be required.
IAM & Billing
IAM stands for Identity Access Management, every Cloud provider such as Amazon and Azure have their own access management solutions to manage the different members on the platform. Each member has roles and permissions assigned to them to allow them suitable access to perform their duties on the platform.
On GCP IAM, there are 3 commonly used member types that we may grant access to and they are:
- Google account (Single person): is a single person with a gmail account. Grant roles and permissions to a gmail account
- Service account (Not a person): This member is non-human and belongs to the application, we may require a Robot to perform actions on our platform
- Google Group (Multiple people): a collection of google accounts and service accounts. This group has a unique email address that is part of the group. Quick way to grant the same role/permissions to a group of users.
Roles and Permissions
In GCP IAM, we grant roles to members for them to perform their duties. Roles are made up of a list of permissions which are very specific.
There are already many pre-made or pre-defined roles readily available for us to use. However we can also create custom roles if we find that the existing roles are insufficient.
We can also edit the list of permissions for each role.
Primitive roles
There are three primitive or base roles that can be applied to members:
- Owner - Full access to resources (can manage roles)
- Editor - Edit access to resources (change or add etc)
- Viewer - Read access to resources
Every resource must belong to a project and a project must have a billing account attached to it. If we grant a member access on a higher hierarchy level. That member has access to all levels below that hierarchy level as well.
Billing
Billing accounts are attached to projects, and any costs incurred from a project are billed to the payment method on the attached billing account. Spending limits or budgets can be set for a day. The billing is done monthly, summing all the daily charges and taxes etc.
Charges across projects if billing accounts for the projects are different is simple. Whichever project initiates the process of transferring data across the projects will be charged the transferal fee.
Cloud BigQuery
BigQuery is Google Cloud Platform’s Data-warehousing solution. It is meant for Big data analytics that is lightning fast at processing and perfect for forming the dataset behind dashboards.
It is serverless and scales massively to over PetaBytes of storage. It is relatively cheap to store data however, the real cost comes when we want to process the data.
BigQuery allows for batch and streaming inserts where batch is for free and streaming is not. Hence we should only use streaming when absolutely necessary.
Pricing Structure
BigQuery offers scalable, flexible pricing options to help fit our project and budget. BigQuery charges for data storage, streaming inserts, and for querying data, but loading and exporting data are free of charge.
Storage is relatively cheap only 2 cents per GB. However, the query is very expensive especially when we have big data sets that are a few TBs. Moving data in and out of BigQuery is free and only streaming inserts charge.
Authorized Views. Giving a view access to a dataset is also known as creating an authorized view in BigQuery. An authorized view allows us to share query results with particular users and groups without giving them view or edit access to the underlying tables that made that view.
Partitioned Tables
Partitioned tables in BigQuery allows a single table to be split up into “partitions”, BigQuery offers date-partitioned tables so the partitions are separated on each day. For example Monday will be in one partition while Tuesday will be on another partition.
Why do we need partitioned tables? The reason is to target a small section of the table to increase the query performance (it’s faster) and reduce the cost per query. Cost is based on how much data we read/process hence if we only look at a section of the table it will reduce the cost accordingly.
Partition table limits. Each partitioned table can have up to 2,500 partitions that is 2500 days or a few years.
Daily limit. 2000 partition updates per table, per day.
Rate limit. 50 partition updates every 10 seconds.
_PARTITIONTIME Pseudo column
Partitioned tables include a pseudo column named _PARTITIONTIME that contains a date-based timestamp for data loaded into the table. For example, if data is appended to a table on April 15, 2016, all of the rows of data appended on that day contain the value TIMESTAMP("2016-04-15") in the _PARTITIONTIME column.
Pseudo columns are reserved for the table and cannot be used by the user. We will not be able to see it if we do not select it explicitly with an alias.
Use of Pseudo column. Select temp from mydataset.temps where _PARTITIONTIME between TIMESTAMP('2016-01-01') and TIMESTAMP('2016-01-02');
Wildcard Tables
Wildcard tables are used if we want to union all similar tables with similar names. The reason why we would want to do this is because if there are say 50 tables that we want to query at once we will have to union them all so we would have to type out all their names. It gets tedious.
Example: Select Column1 From 'project.dataset.Table*' where Column1 == "some variable"
Reducing processing cost
How do we reduce processing/reading cost for BigQuery especially for Datasets that are very big?
- Use Preview options (don’t run queries to explore data)
- Use Query Validator to check the price of the query before running it
- Always consider partitioned tables, so we can filter via the date pseudo column
- Try avoiding
Select *clause as this selects all columns and will increase cost, try to select only the columns we need - We can hard limit project bytes processed per day. If we exceed the query will return an Error
- We can hard limit members or users as well
Could Datalab
Cloud datalab is built on Jupyter notebook which is an open source python based data processing/analysis tool. We can use Python, SQL and Javascript to process the data.
It runs on an instance or VM using Google Compute Engine and can be connected to BigQuery, Google Compute Engine and Google Cloud storage. It is a free tool to use, however normal charges still apply for using BigQuery datasets while processing the data and running VMs.
Cloud Datastudio
Data-studio is GCP’s dashboarding solution where we showcase the dataset and create reports for clients or colleagues. Data studio is similar to Tableau however Tableau has many more features than data studio.
Data studio sources (base datasets) can come from: BigQuery, MySQL, CloudSQL, Google sheets, Google analytics etc.
The update is automatic, that is if the source data changes the dashboard will also change according to the data. Which is very useful. Also, we must have the right Roles/Permissions to access the resources accordingly.
Sharing reports
Data studio makes it extremely simple to share the reports as data studio is stored on Google Drive and we can share it as simply as sharing other files on Google Drive.
We can limit the viewers view permission to the underlying data source so that they must also have the right permissions to see the data source or they can borrow our permissions to see the data source.
Cloud Pub/Sub
Google Cloud Pub/Sub is a fully-managed real-time messaging service that allows us to send and receive messages between independent applications. In doing so, the sender and receiver is “decoupled”. Decoupling has many advantages such as allowing secure and high availability between the sender and receiver. Cloud Pub/Sub has many similar competitors such as AWS SQS (Simple Queue Service) and the open source Apache Kafka.
Publisher will keep publishing messages to the topic and form a queue within Pub/Sub then the subscriber will try to consume the messages and once it has acknowledged that it has consumed the message it will be deleted from the queue. Could Pub/Sub guarantees that the subscriber will receive the message at least once before being deleted from the queue.
What do we mean by decoupling and how does it improve the overall structure, reliability and availability?
As it stands now Pub/Sub allows for decoupling between Publisher and Subscriber. For example, if the Publisher were to be changed to another publisher what will happen to the architecture? The short answer is nothing. Very little work is required to change the publisher. The same goes for adding multiple publishers to existing architectures with just one subscriber. However if publisher and subscriber were “tightly-coupled” then changing publisher or subscriber will require major code and architectural changes.
Pub/Sub benefits:
- Durable and low latency (its fast response)
- Global Presence (can use anywhere in the world)
- Data reliability (guarantees we get the message at least once from the publisher)
- Security (Encryption of data at rest and on the move)
Hadoop & Cloud Dataproc
What is Hadoop? Before we start to understand Cloud Dataproc we need to first understand what is Hadoop. Hadoop is the name given to the biggest open source big data system or distributed computing system under the Apache foundation. The name Hadoop actually came from one of the founder’s son’s toy elephant.
The core foundation of Hadoop is its HDFS or Hadoop distributed file system. The Hadoop ecosystem is based on interacting with the HDFS.
What is HDFS? HDFS is a distributed computing software that utilizes many nodes/computers/VMs hard drive capacity and memory to store and process big data. The Hadoop distributed file system is installed on top of many nodes and “combines” a major proportion of their data storage capacity so that it seems like just one file system instead of many file systems (one for each node). Through this combined file system called HDFS we can store large amounts of data and process the data.
To put this in simpler terms. Our computer may have a memory of 16GB and a hard drive capacity of 1 TB. Now if we need to store 1000TB or 1 PetaByte how would we do it? Just use 1000 computers? But if so do we need to log in to all the computers and access their data when we need access to them? That will take way too long and it’s inconvenient. That is what HDFS aims to solve and remember this is open source.
HIVE
Apache Hive is an open-source data warehouse system for querying and analyzing large datasets stored in HDFS. Hive supports HiveQL which is like SQL, HiveQL is then translated to map-reduce jobs in the background.
Map-reduce is a data processing technique used commonly to extract, transform, and load data on Hadoop.
PIG
Pig is a high level scripting language that is used with Apache Hadoop. Pig enables data workers to write complex data transformations without knowing Java. Pig’s simple SQL-like scripting language is called Pig Latin, and appeals to developers already familiar with scripting languages and SQL.
OOZIE & SQOOP
Oozie is a workflow scheduler system to manage Apache Hadoop jobs.
Sqoop transfers large amount of data into Hdfs from relational databases such as MySQL. It is a transferring framework.
Dataproc
Dataproc is a fully managed cloud service for running Apache Hadoop clusters. We only pay for the resources we use with per-second billing (for the VMs). We can also scale easily if required. Dataproc offers an easy solution for customers with existing Hadoop workloads to transfer their workload onto GCP without having to rewrite all their code and spend a lot of time moving to GCP.
Cloud Dataflow
Cloud Dataflow is a fully-managed service for transforming data via streaming (real-time) or batch modes with reliability and auto-scaling/serverless as needed.
Cloud Dataflow shines especially in streaming applications and commonly sits between the “front end services/customer facing solutions usually high throughput” and the “backend services/Data Storage solutions like BigQuery”.
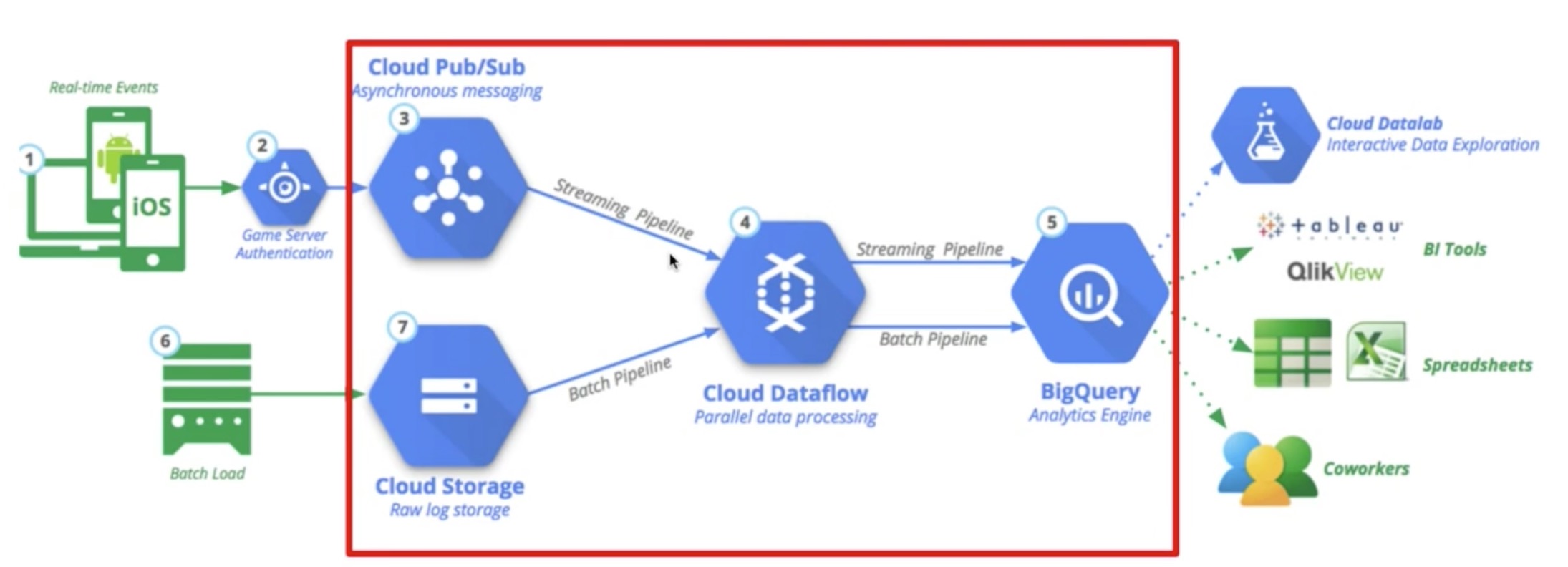
Cloud Dataflow takes input from Pub/Sub and Cloud Storage via streaming and batch modes, processes them, and then pushes them to BigQuery to store and analyze. Note that it is doing parallel data processing.
You might ask, BigQuery already allows streaming inserts and batch inserts so why do we need Cloud Dataflow at all? Isn’t that just in the way? We can just connect Pub/Sub and Cloud Storage straight to BigQuery.
Well no we can’t, because the source data might be in the wrong format to be able to store in our storage solutions so a data transformation stage is required between source and storage. This is where Cloud Dataflow comes in. It helps transform the data, streaming or batch into the correct format to be useful in BigQuery. Especially for streaming transformations as this is not really well handled before in the data scene with only a handful of other products such as Apache Nifi and Storm that are open sourced.
Stackdriver
Stackdriver is GCP’s monitoring, logging and diagnostics solution. It gives us the insight into the health, performance and availability of our GCP applications, which helps us solve issues faster.
Main Stackdriver functions:
- Debugger
- Error reporting
- Monitoring
- Alerting
- Tracing
- Logging
Debugger. Stackdriver debugger allows us to inspect the state of a running application in real time without stopping or slowing it down. We can use it to see the code behavior in production.
Error Reporting. Error reporting counts, analyzes and aggregates the crashes in our cloud services. We can see the errors in a management interface provided by Stackdriver. We can also receive emails and mobile alerts on new errors.
Monitoring. Monitoring provides an overview of performance, uptime and health of our cloud services. It collects metrics, events and metadata from GCP, AWS and other popular open source softwares. It ingests these metrics and displays them via a dashboard.
Alerting. Alerting allows us to create policies to notify us when the health and uptime check results go over a certain limit. The alerts can be notifications sent to Slack, Camfire, HipChat and PagerDuty.
Tracing. Tracing tracks how requests propagate through our application and receive detailed near real time performance insights. It auto analyses to generate latency reports to show us performance degradations on the VMs. What this means is that if our VM or app slows down tracing will pick this up.
Logging. Logging allows us to store, search, analyse, monitor and alert on log data and events from GCP. Logging is fully-managed that can scale and ingest logs from thousands of VMs. We can also analyze this in real-time.
Machine Learning/AI & Tensroflow
Google’s AI products:
- Cloud Natural Language API
- Cloud Translation API
- Cloud Vision API
- Cloud Speech API
Cloud Natural Language API
Helps us analyze sentences in a chat or messages. It analyses the sentence in four categories: sentiment, category, entity, and syntax. Sentiment is whether the user is “happy” or “angry” etc. Category is what is the message talking about. Entity is what is in the message for example “empire state building”, syntax is the structure of the sentence itself.
Cloud Translation API
Have you used google translate? This is basically it. It helps translate one language into another.
Cloud Vision API
It helps recognize the different objects within pictures and the text written in the pictures.
Cloud Speech API
This product helps to translate speech into text. So auto caption will require this API or similar APIs to turn speech to text.